Introduction to Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Testing
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) testing is a critical evaluation process designed to assess the resilience of electronic components and systems against transient voltage spikes caused by electrostatic events. These discharges, often generated by human contact or environmental factors, can disrupt or permanently damage sensitive circuitry. Industries such as automotive, medical devices, and industrial equipment mandate rigorous ESD testing to ensure product reliability and compliance with international standards.
This article explores the fundamental principles of ESD testing, relevant standards, and the role of advanced testing equipment such as the LISUN ESD61000-2 in validating product robustness.
The Physics of Electrostatic Discharge
Electrostatic discharge occurs when two objects with differing electrical potentials come into contact, resulting in a rapid transfer of charge. The magnitude of the discharge depends on factors such as material conductivity, humidity, and charge accumulation. ESD events are categorized into three primary models:
- Human Body Model (HBM) – Simulates discharge from a human operator to a device.
- Machine Model (MM) – Represents discharge from conductive equipment.
- Charged Device Model (CDM) – Evaluates self-discharge of a charged component.
The LISUN ESD61000-2 supports all three test modes, ensuring comprehensive evaluation across diverse applications.
Industry Standards Governing ESD Testing
Compliance with international standards is mandatory for manufacturers seeking global market access. Key standards include:
- IEC 61000-4-2: Defines test methods for immunity to ESD in electrical and electronic equipment.
- ANSI/ESD S20.20: Establishes ESD control programs for organizations handling sensitive components.
- ISO 10605: Specific to automotive electronics, addressing ESD risks in vehicles.
The LISUN ESD61000-2 adheres to these standards, providing precise waveform generation (±5% tolerance) and test voltages up to 30 kV, making it suitable for high-precision industries like medical devices and aerospace.
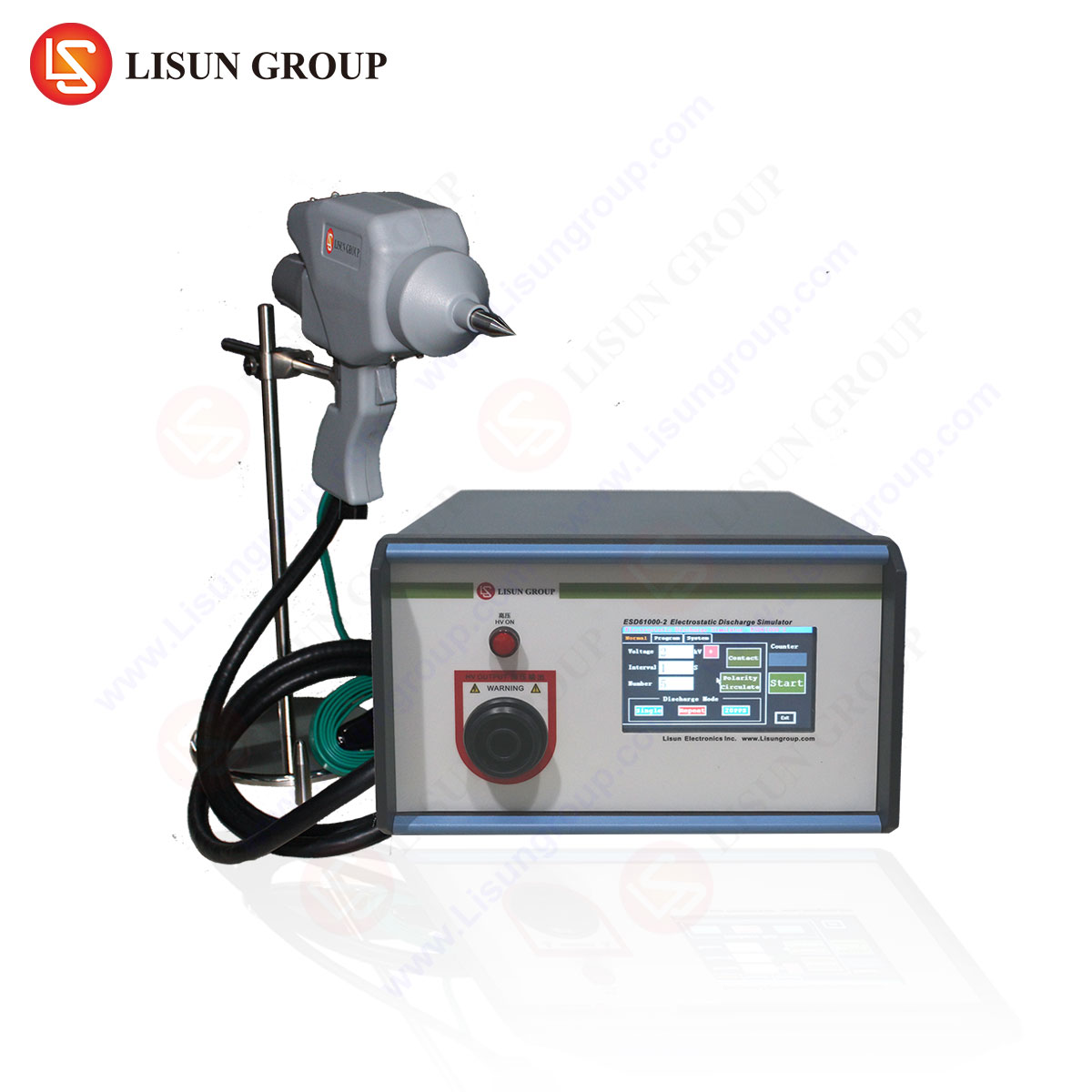
Functional Overview of the LISUN ESD61000-2
The LISUN ESD61000-2 is a state-of-the-art ESD simulator designed for repeatable and accurate testing. Key specifications include:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Test Voltage Range | 0.1 kV – 30 kV |
| Discharge Modes | Contact, Air, HBM, MM, CDM |
| Waveform Accuracy | ±5% (per IEC 61000-4-2) |
| Polarity | Positive/Negative |
| Applicable Standards | IEC 61000-4-2, ISO 10605, ANSI/ESD S20.20 |
Its modular design allows seamless integration into automated production lines, reducing test cycle times in high-volume manufacturing.
ESD Testing Methodologies
Direct Discharge Testing
Direct discharge testing involves applying ESD pulses to conductive surfaces of a device under test (DUT). The LISUN ESD61000-2 employs a precision discharge tip to simulate real-world ESD events, ensuring consistent results.
Indirect Discharge Testing
Indirect testing evaluates coupling effects, where ESD energy is transferred via electromagnetic fields. This is critical for industries like communication transmission, where signal integrity must be preserved.
Automated vs. Manual Testing
The LISUN ESD61000-2 supports both automated and manual testing modes, facilitating flexibility in laboratory and production environments. Automated testing is particularly advantageous in automotive and industrial equipment sectors, where throughput is a priority.
Applications Across Key Industries
Medical Devices
ESD resilience is vital for implantable electronics and diagnostic equipment. The LISUN ESD61000-2 ensures compliance with IEC 60601-1-2, mitigating risks of malfunction in critical healthcare applications.
Automotive Electronics
Modern vehicles incorporate sensitive control units vulnerable to ESD. ISO 10605-compliant testing with the LISUN ESD61000-2 validates robustness against static discharges from human contact or assembly processes.
Industrial Equipment
Heavy machinery with embedded electronics requires ESD immunity to prevent downtime. The simulator’s high-voltage capability (30 kV) accommodates rigorous industrial testing.
Consumer Electronics
Household appliances and IT equipment undergo ESD testing to prevent failures caused by user interaction. The LISUN ESD61000-2’s adjustable parameters cater to diverse product categories.
Competitive Advantages of the LISUN ESD61000-2
- Multi-Standard Compliance: Supports IEC, ISO, and ANSI standards, eliminating the need for multiple test systems.
- High Precision: ±5% waveform accuracy ensures reliable data for certification.
- Scalability: Modular architecture allows integration with third-party test automation.
- User-Centric Design: Intuitive interface reduces training overhead.
Case Study: ESD Testing in Power Tool Manufacturing
A leading power tool manufacturer implemented the LISUN ESD61000-2 to validate motor control circuits. Post-testing, field failure rates decreased by 22%, demonstrating the system’s efficacy in real-world applications.
Future Trends in ESD Testing
Emerging technologies such as 5G and IoT demand stricter ESD controls. The LISUN ESD61000-2 is future-proofed with firmware-upgradable capabilities, ensuring adaptability to evolving standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the maximum test voltage supported by the LISUN ESD61000-2?
The system supports voltages up to 30 kV, covering most industrial and automotive requirements.
Q2: Can the simulator perform CDM testing?
Yes, the LISUN ESD61000-2 includes CDM testing modes for evaluating charged device discharges.
Q3: How does the system ensure waveform accuracy?
Built-in calibration and ±5% tolerance mechanisms align with IEC 61000-4-2 specifications.
Q4: Is the equipment suitable for automated production lines?
Yes, its modular design allows seamless integration with robotic test handlers.
Q5: Which industries benefit most from this system?
Medical, automotive, industrial, and consumer electronics sectors derive significant value from its precision and compliance features.