Introduction to Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Testing
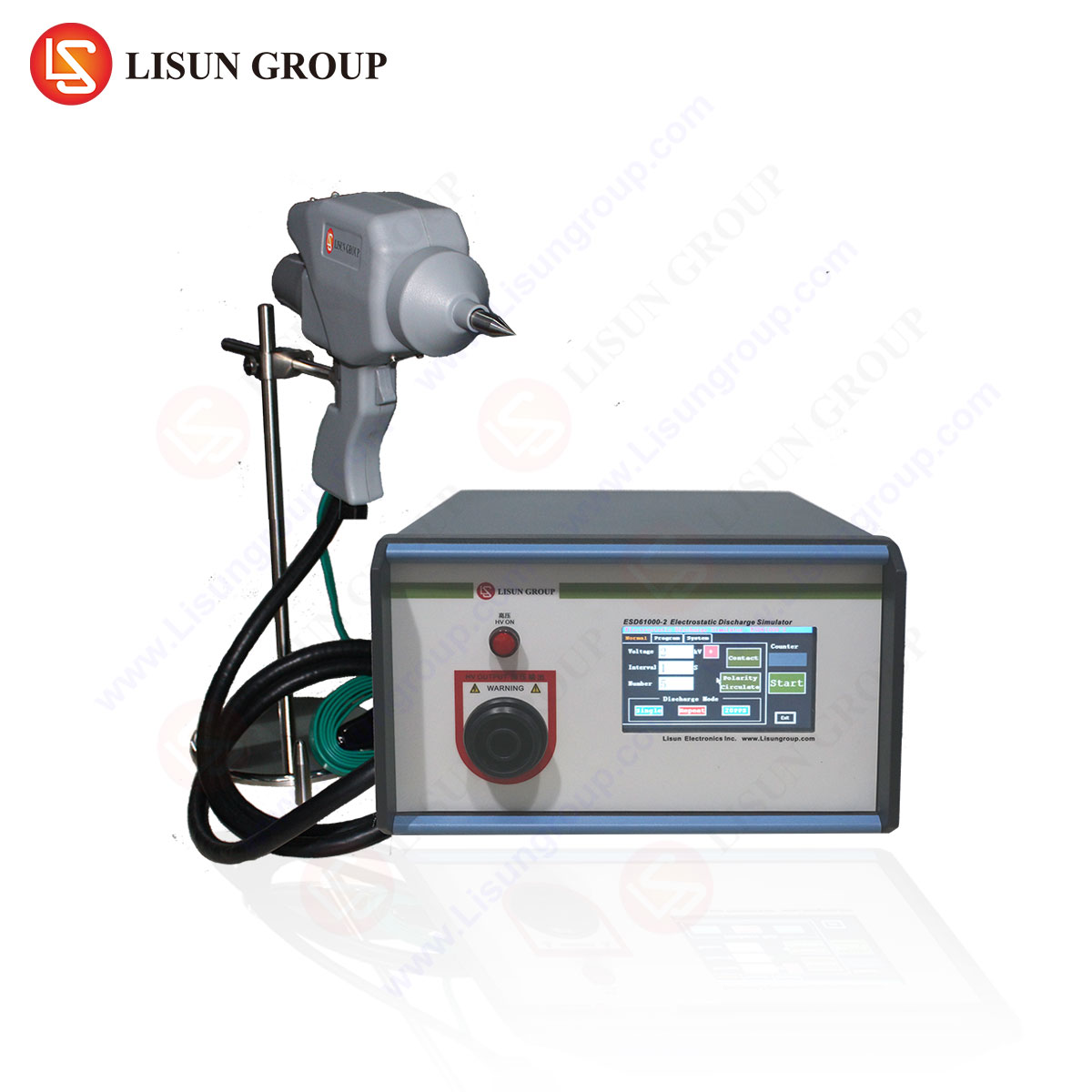
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a critical phenomenon in electronics manufacturing, where sudden current flows between objects at different electrostatic potentials can damage sensitive components. ESD guns, also known as ESD simulators, replicate these transient events to evaluate the immunity of electronic devices under standardized test conditions. This article examines the technical features of ESD guns, with a focus on the LISUN ESD61000-2, a high-precision instrument designed for compliance testing across multiple industries.
Core Functional Features of ESD Guns
High-Voltage Discharge Waveform Reproducibility
The LISUN ESD61000-2 generates repeatable discharge waveforms in compliance with IEC 61000-4-2, ensuring accurate simulation of human-body model (HBM) ESD events. Key waveform parameters include:
- Rise Time: 0.7–1 ns
- Peak Current: Up to 30 A (for 8 kV contact discharge)
- Discharge Modes: Contact and air discharge
This precision is essential for validating devices in sectors such as medical equipment and automotive electronics, where waveform fidelity impacts test reliability.
Adjustable Test Parameters for Multi-Standard Compliance
The ESD61000-2 supports configurable voltage levels (0.1–30 kV) and discharge intervals (0.05–1 s), accommodating standards such as:
- IEC 61000-4-2 (General ESD immunity)
- ISO 10605 (Automotive ESD testing)
- ANSI/ESD STM5.1 (Component-level HBM testing)
This flexibility enables cross-industry applications, from household appliances to rail transit systems.
Testing Principles and Methodologies
Direct and Indirect Discharge Modes
ESD testing involves two primary methodologies:
- Contact Discharge: A grounded tip directly injects current into the device under test (DUT).
- Air Discharge: The ESD gun approaches the DUT until a spontaneous arc occurs, simulating real-world ESD events.
The ESD61000-2 integrates both modes with automatic polarity switching (± polarity), critical for industrial equipment subjected to variable electrostatic environments.
Grounding and Environmental Controls
Proper grounding (≤ 1 Ω resistance) and humidity (30–60% RH) are mandated by IEC 61000-4-2 to minimize test variability. The ESD61000-2 includes a real-time environmental monitoring system, ensuring adherence to laboratory-grade conditions for aerospace and IT equipment validation.
Industry-Specific Applications
Medical Devices and Patient Safety
ESD-induced failures in defibrillators or infusion pumps can have life-threatening consequences. The ESD61000-2’s ±15 kV air discharge capability verifies compliance with IEC 60601-1-2, mitigating risks in clinical environments.
Automotive Electronics and ISO 10605
Modern vehicles integrate sensitive ADAS sensors and infotainment systems. The ESD61000-2’s 30 kV range exceeds ISO 10605’s 25 kV requirement, ensuring robustness against high-energy discharges in electric vehicle powertrains.
Consumer Electronics and IEC 61000-4-2
For smart home devices and audio-visual equipment, the ESD61000-2’s 150 pF / 330 Ω network replicates human-body discharges, identifying vulnerabilities in PCB layouts or shielding.
Competitive Advantages of the LISUN ESD61000-2
Enhanced Accuracy with Digital Feedback Control
Unlike analog-based competitors, the ESD61000-2 employs closed-loop digital control, reducing waveform distortion (< ±5% deviation). This is critical for instrumentation manufacturers requiring sub-nanosecond timing precision.
Modular Design for Custom Test Setups
Interchangeable tips (4 mm round, 8 mm hemispherical) and remote triggering support integration into automated test systems for high-volume production lines in LED lighting and power tools.
Compliance with Emerging Standards
The ESD61000-2 pre-validates against draft revisions of AEC-Q200 (passive components) and MIL-STD-883 (military-grade ESD), future-proofing R&D investments.
Technical Specifications of the LISUN ESD61000-2
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Voltage Range | 0.1–30 kV (± polarity) |
| Discharge Modes | Contact / Air (automatic detection) |
| Waveform Compliance | IEC 61000-4-2, ISO 10605 |
| Current Rise Time | 0.7–1 ns |
| Environmental Monitoring | Built-in RH/temperature sensors |
| Interfaces | RS-232, Ethernet (remote control) |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How does the ESD61000-2 ensure consistent air discharge distances?
The gun’s motorized approach system maintains a 1 mm/s advance rate, eliminating manual errors per IEC 61000-4-2 Clause 6.2.
Q2: Can the ESD61000-2 test insulated devices?
Yes, indirect discharge via horizontal coupling planes (HCP/VCP) evaluates non-conductive enclosures in household appliances.
Q3: What industries mandate ESD61000-2 testing?
Medical (IEC 60601), automotive (ISO 10605), and telecom (EN 55035) sectors require it for CE/FCC certification.
Q4: How is waveform accuracy verified?
Third-party calibration using a 1 GHz oscilloscope and current target (per IEC 61000-4-2 Annex A).
Q5: Does the ESD61000-2 support non-standard pulse shapes?
Custom waveforms (e.g., 500 pF/500 Ω for spacecraft components) are programmable via PC software.