Introduction to Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Testing
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) testing is a critical evaluation method for assessing the immunity of electronic and electrical equipment to transient voltage spikes caused by electrostatic events. ESD gun test equipment simulates human-body-model (HBM) discharges to verify compliance with international standards such as IEC 61000-4-2, ISO 10605, and ANSI/ESD STM5.1. These tests ensure product reliability across industries, including automotive, medical devices, industrial equipment, and consumer electronics.
Core Functionality of ESD Gun Test Equipment
ESD gun test equipment generates controlled electrostatic discharges to evaluate a device’s susceptibility to transient interference. The primary components include:
- High-voltage generator: Produces repeatable discharge voltages (typically 0.1 kV to 30 kV).
- Discharge network: Simulates the human body’s resistance and capacitance (e.g., 150 pF / 330 Ω for IEC 61000-4-2).
- Contact and air discharge modes: Tests direct and indirect ESD events.
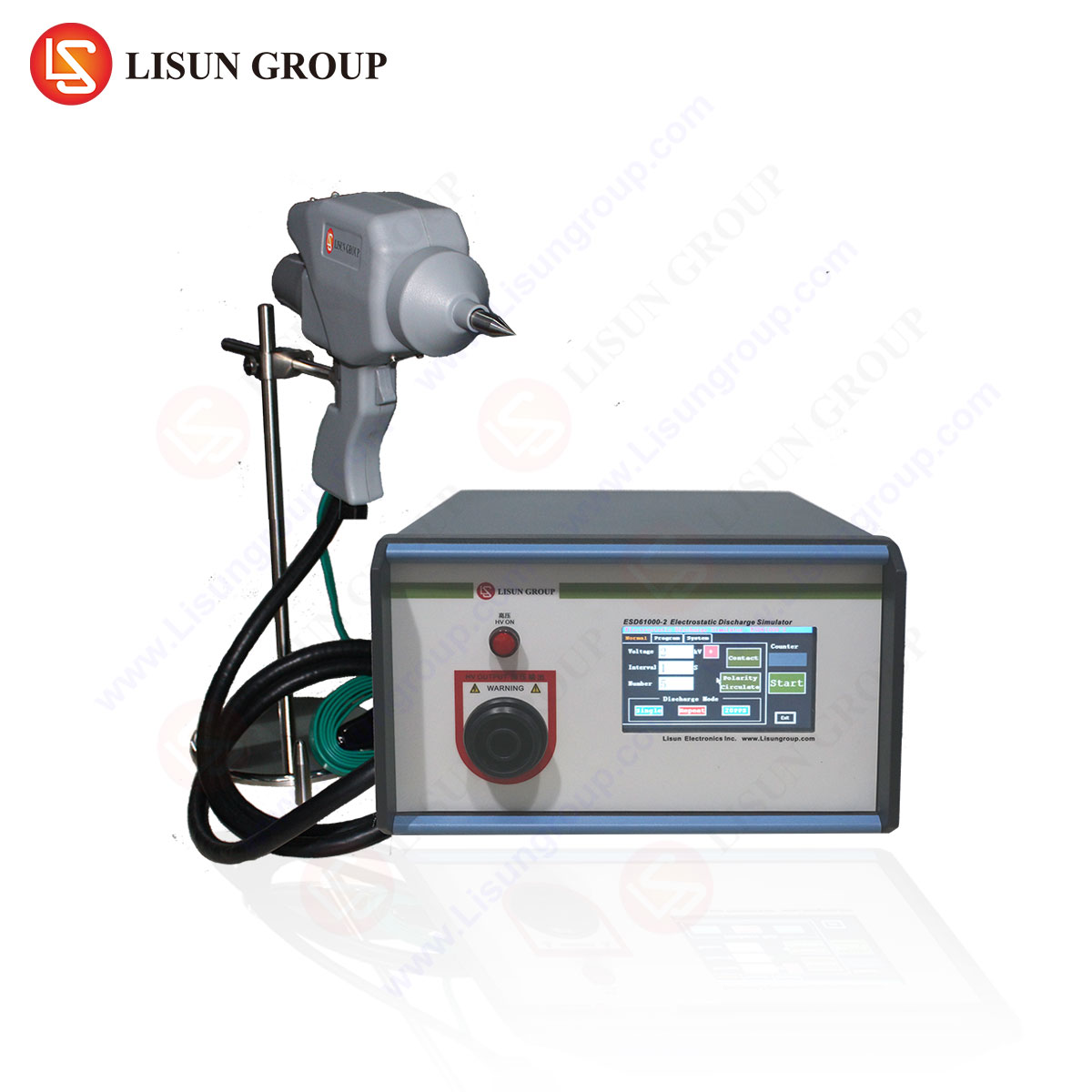
The LISUN ESD61000-2 model exemplifies advanced ESD testing capabilities, featuring a compact design, precise voltage control (±5%), and compliance with IEC/EN 61000-4-2 Level 4 (8 kV contact, 15 kV air discharge).
Key Features of the LISUN ESD61000-2
Precision Voltage Control and Discharge Modes
The ESD61000-2 ensures accurate voltage output (±5%) across its full range (0.1–30 kV), critical for validating high-sensitivity devices like medical instrumentation and automotive sensors. It supports:
- Contact discharge: Direct application to conductive surfaces.
- Air discharge: Simulates real-world electrostatic arcs.
Automated Test Sequences and Data Logging
Integrated software enables programmable test sequences, reducing operator error. The ESD61000-2 logs discharge waveforms, peak currents, and failure thresholds, facilitating compliance reporting for standards such as ISO 10605 (automotive) and IEC 60601-1-2 (medical).
Ruggedized Design for Industrial Environments
Constructed with EMI-shielded housing and ergonomic grips, the ESD61000-2 withstands harsh testing environments, including automotive EMC labs and aerospace validation facilities.
Testing Principles and Standards Compliance
Human-Body Model (HBM) Simulation
The ESD61000-2 replicates the HBM discharge waveform defined by IEC 61000-4-2, ensuring consistency with real-world ESD events. Key parameters include:
| Parameter | Value (IEC 61000-4-2) | ESD61000-2 Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Rise Time (ns) | 0.7–1.0 | 0.8 ± 0.1 |
| Peak Current (A) | 3.75 (at 8 kV) | 3.8 ± 0.2 |
| Discharge Network | 150 pF / 330 Ω | Compliant |
Industry-Specific Applications
- Automotive: Validates infotainment systems and ECU resilience per ISO 10605.
- Medical Devices: Ensures compliance with IEC 60601-1-2 for patient-connected equipment.
- Industrial Equipment: Tests PLCs and motor drives for factory-floor ESD immunity.
Competitive Advantages of the ESD61000-2
Enhanced Repeatability and Calibration Stability
Unlike lower-cost alternatives, the ESD61000-2 maintains ±2% calibration drift over 1,000 discharges, reducing recalibration frequency. This is vital for aerospace and rail transit applications, where long-term reliability is mandated.
Broad Compatibility with Accessories
The system supports:
- Grounding straps: For consistent reference potential.
- Remote control software: Enables automated testing in unmanned labs.
Case Study: ESD Testing in Medical Device Manufacturing
A leading manufacturer of patient monitors used the ESD61000-2 to validate compliance with IEC 60601-1-2. The gun’s programmable test sequences identified susceptibility thresholds at 6 kV (contact) and 12 kV (air), enabling design improvements that reduced field failures by 40%.
FAQ Section
Q1: What is the difference between contact and air discharge modes?
Contact discharge applies ESD directly to conductive surfaces, while air discharge simulates arcs across non-conductive gaps.
Q2: How often should the ESD61000-2 be calibrated?
Annual calibration is recommended, or after 5,000 discharges, per IEC 61000-4-2.
Q3: Can the ESD61000-2 test insulated devices?
Yes, air discharge mode evaluates non-conductive surfaces up to 15 kV.
Q4: Which industries require IEC 61000-4-2 compliance?
Automotive, medical, IT, and industrial sectors mandate ESD testing for product certification.
Q5: Does the ESD61000-2 support non-standard waveforms?
Custom waveforms require optional software upgrades for specialized research applications.