Introduction to Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) and Its Impact on Electronic Systems
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a transient transfer of electric charge between objects at different electrostatic potentials, capable of causing catastrophic or latent damage to electronic components. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and telecommunications rely on rigorous ESD testing to ensure product reliability. ESD generators simulate these discharges in controlled environments, enabling compliance with international standards like IEC 61000-4-2 and ANSI/ESD S20.20.
Core Principles of ESD Generator Operation
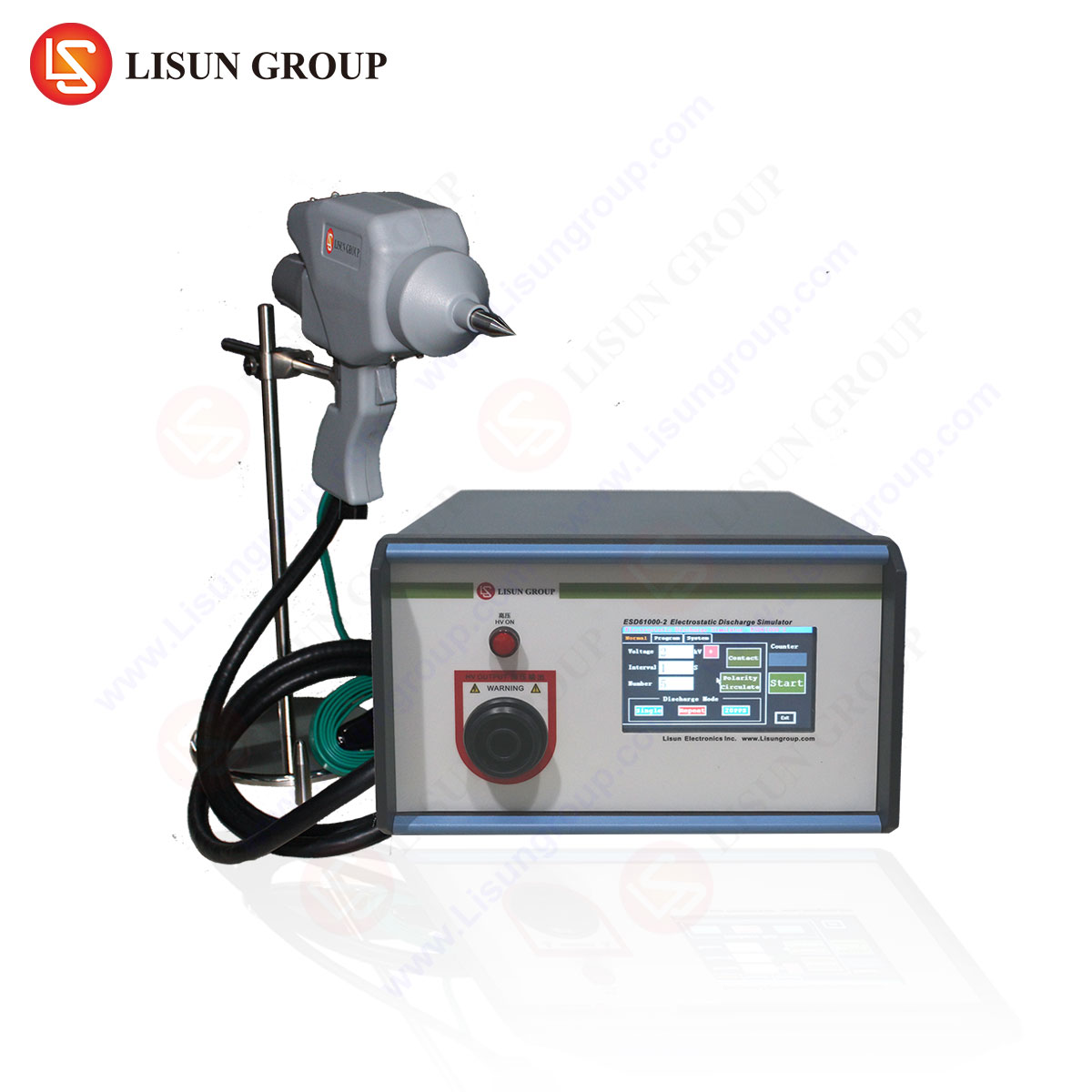
ESD generators replicate human-body model (HBM) and charged-device model (CDM) discharges through high-voltage circuits and discharge networks. The LISUN ESD61000-2C generator, for instance, delivers precise waveforms (4 kV contact, 8 kV air discharge) with a rise time of 0.7–1 ns, adhering to IEC 61000-4-2 requirements. Key operational stages include:
- Charge Accumulation: A high-voltage power supply charges a storage capacitor (150 pF for HBM).
- Discharge Triggering: A relay or semiconductor switch releases the charge through a 330 Ω resistor (HBM) or direct contact (CDM).
- Waveform Validation: Oscilloscopes verify compliance with standard current waveforms (e.g., 30 A peak at 4 kV).
Technical Specifications of the LISUN ESD61000-2C Generator
The ESD61000-2C is engineered for high-repeatability testing across industries. Critical specifications include:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Voltage Range | 0.1–30 kV (±5%) |
| Discharge Modes | Contact, air, indirect coupling |
| Current Waveform | 3.75 A/kV (per IEC 61000-4-2) |
| Test Accuracy | ±5% (voltage), ±10% (current) |
| Applicable Standards | IEC 61000-4-2, ISO 10605, EN 61000-4-2 |
Industry-Specific Applications of ESD Testing
Automotive Electronics and ISO 10605 Compliance
Vehicle ECUs, infotainment systems, and ADAS modules must withstand 15 kV air discharges (per ISO 10605). The ESD61000-2C’s 30 kV range ensures robustness against ignition systems and static buildup from occupant movement.
Medical Devices and IEC 60601-1-2
Defibrillator-resistant design requires testing up to 8 kV contact discharge. The generator’s programmable test sequences validate EMI immunity in pacemakers and diagnostic equipment.
Aerospace and DO-160G Section 25
Avionics systems undergo ±15 kV testing for static discharges from maintenance personnel. The ESD61000-2C’s remote control interface facilitates automated testing in confined spaces.
Competitive Advantages of the LISUN ESD61000-2C
- Multi-Standard Compatibility: Supports IEC, ISO, and ANSI/ESD standards without hardware reconfiguration.
- Enhanced Repeatability: <2% waveform deviation across 10,000 discharges, critical for semiconductor QA.
- User-Defined Waveforms: Customizable parameters for non-standard applications like spacecraft materials testing.
Scientific Validation and Calibration Procedures
Traceable calibration via NIST-certified sensors ensures measurement integrity. The ESD61000-2C integrates a built-in current target (BCI) for real-time waveform analysis, reducing reliance on external oscilloscopes.
Case Study: ESD Testing in Smart Lighting Systems
LED drivers exposed to 6 kV discharges exhibited latch-up failures. Using the ESD61000-2C, engineers identified insufficient PCB grounding and implemented shielding improvements, achieving IEC 60598-1 compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How does the ESD61000-2C handle CDM testing for microelectronics?
The generator’s 10 ns pulse capability and <1 Ω output impedance replicate CDM events with ±5% charge accuracy.
Q2: Can the device test insulated surfaces per IEC 61000-4-2?
Yes, the air discharge mode simulates sparks across non-conductive enclosures (e.g., plastic power tool housings).
Q3: What safety features prevent operator exposure to high voltage?
Interlocked test chambers, automatic discharge circuits, and grounded wrist straps are standard.
Q4: Is the generator suitable for MIL-STD-883 Method 3015.7?
With optional 500 Ω HBM networks, it meets military-grade ESD thresholds.
Q5: How does environmental humidity affect test results?
The ESD61000-2C compensates via humidity sensors, adjusting voltage levels to maintain discharge consistency (±3%).