Introduction to Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Testing
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) testing is a critical evaluation process for ensuring the reliability and durability of electronic and electrical components across multiple industries. ESD events can cause latent or catastrophic failures in sensitive devices, necessitating rigorous testing protocols. This guide examines the principles, methodologies, and equipment used in ESD testing, with a focus on the LISUN ESD61000-2 ESD Gun, a high-precision instrument designed for compliance with international standards.
Fundamentals of ESD Testing and Industry Standards
ESD testing simulates real-world electrostatic discharge events to assess a device’s immunity to transient electrical surges. The primary standards governing ESD testing include:
- IEC/EN 61000-4-2: Defines test levels and methodologies for ESD immunity.
- ANSI/ESD S20.20: Establishes electrostatic control programs for manufacturing.
- ISO 10605: Specific to automotive ESD testing.
- AEC-Q100-002: Focuses on semiconductor component reliability.
These standards dictate test parameters such as discharge voltage (ranging from 2 kV to 30 kV), waveform characteristics (rise time ≤ 1 ns), and environmental conditions (humidity, temperature).
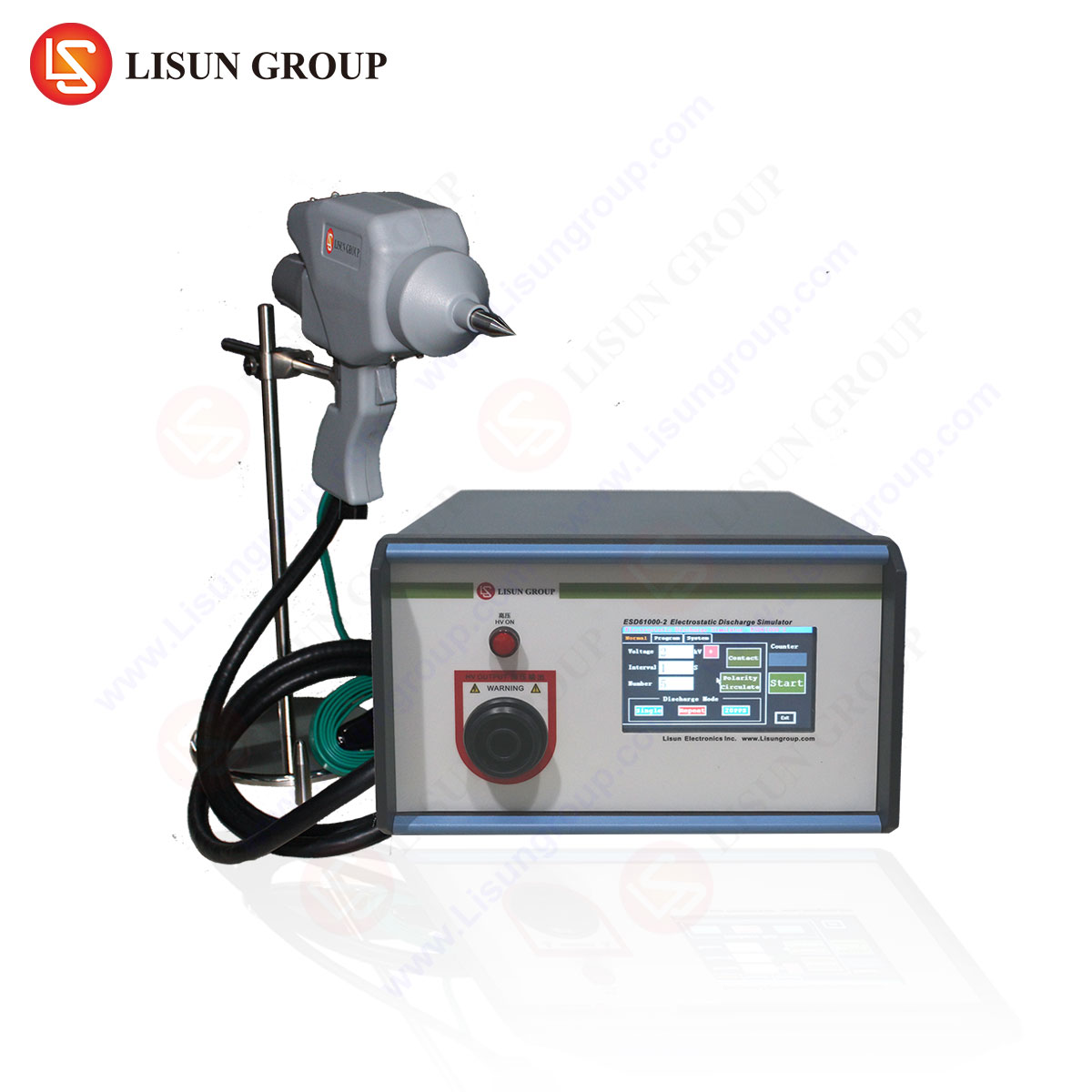
LISUN ESD61000-2 ESD Gun: Technical Specifications
The LISUN ESD61000-2 ESD Gun is engineered for precision compliance with IEC 61000-4-2 and related standards. Key specifications include:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Discharge Voltage Range | 0.1 kV – 30 kV |
| Discharge Modes | Contact / Air Discharge |
| Output Current Waveform | Compliant with IEC 61000-4-2 |
| Rise Time | ≤ 1 ns |
| Test Repetition Rate | 1 discharge per second (adjustable) |
| Polarity | Positive / Negative |
| Calibration Accuracy | ±5% |
The device integrates advanced pulse shaping circuitry to ensure accurate waveform replication, critical for validating immunity in high-speed digital circuits.
Testing Methodology: Contact vs. Air Discharge
The LISUN ESD61000-2 supports two primary discharge modes:
-
Contact Discharge
- A direct discharge via a grounded tip.
- Used for conductive surfaces (e.g., metal enclosures in industrial equipment).
- Ensures repeatable, controlled energy transfer.
-
Air Discharge
- Simulates indirect ESD events (e.g., human touch on non-conductive surfaces).
- Applied to insulating materials (plastics in household appliances, medical devices).
- Requires precise distance control (typically 10 mm from the test surface).
Industry-Specific Applications of ESD Testing
Automotive Industry (ISO 10605 Compliance)
Automotive electronics, including infotainment systems and engine control units (ECUs), must withstand ESD events from human interaction or environmental factors. The LISUN ESD61000-2 verifies immunity up to 30 kV, ensuring compliance with ISO 10605.
Medical Devices (IEC 60601-1-2)
Electrosurgical equipment and patient monitors are susceptible to ESD-induced malfunctions. Testing ensures operational safety under electrostatic stress.
Industrial Equipment (IEC 61000-4-2)
Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and motor drives are tested for resilience against ESD in harsh environments.
Consumer Electronics (EN 55024)
Smartphones, audio-video equipment, and IoT devices undergo ESD testing to prevent data corruption or hardware failure.
Competitive Advantages of the LISUN ESD61000-2
- Enhanced Waveform Accuracy
- Meets stringent IEC 61000-4-2 rise time and current requirements.
- Automated Test Sequences
- Programmable discharge patterns for efficiency in high-volume testing.
- Broad Industry Compatibility
- Validated for automotive, aerospace, and medical applications.
- User-Configurable Parameters
- Adjustable voltage, polarity, and discharge intervals.
Case Study: ESD Testing in Power Tools
A leading power tool manufacturer utilized the LISUN ESD61000-2 to evaluate brushless motor controllers. Testing at 8 kV (contact) and 15 kV (air) identified weak points in PCB shielding, leading to design improvements that reduced field failures by 42%.
FAQ: Common Questions on ESD Testing
Q1: What is the difference between contact and air discharge testing?
Contact discharge applies ESD directly to conductive surfaces, while air discharge simulates indirect discharges through insulating materials.
Q2: How often should ESD test equipment be calibrated?
Annual calibration is recommended, per ISO 17025, to maintain measurement accuracy.
Q3: Can the LISUN ESD61000-2 test non-powered devices?
Yes, passive discharge testing is possible, but functional immunity requires powered-state evaluation.
Q4: What industries mandate ESD61000-4-2 compliance?
Medical, automotive, industrial controls, and consumer electronics require adherence.
Q5: Does humidity affect ESD test results?
Yes, low humidity (<30% RH) increases ESD risk, necessitating controlled test environments.
This guide provides a foundational understanding of ESD testing principles, equipment selection, and industry applications, emphasizing the LISUN ESD61000-2 as a benchmark solution for compliance and reliability validation.