Introduction to Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) and Its Impact on Electronic Systems
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a sudden flow of electricity between two electrically charged objects, often caused by contact, electrical shorting, or dielectric breakdown. ESD events can severely damage sensitive electronic components, leading to latent failures, operational disruptions, or catastrophic system breakdowns. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and consumer electronics require rigorous ESD testing to ensure product reliability.
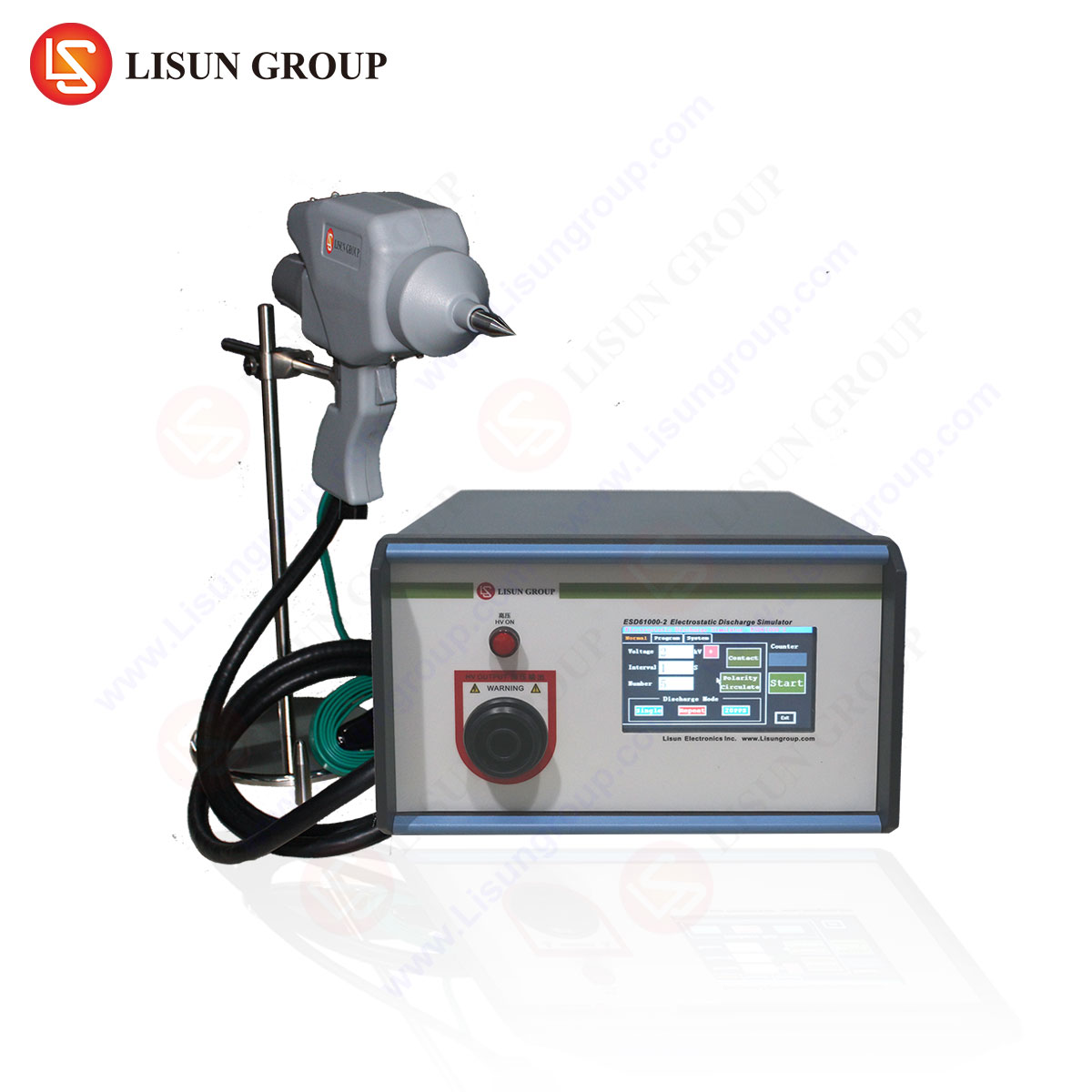
ESD generators, such as the LISUN ESD61000-2, simulate these discharge events under controlled conditions, enabling manufacturers to evaluate product resilience against static electricity. This article examines the technical principles, key features, and applications of ESD generators, with a focus on the ESD61000-2 model.
Fundamental Principles of ESD Testing
ESD testing adheres to international standards, including IEC 61000-4-2, which defines test methodologies for evaluating immunity to electrostatic discharges. The process involves applying controlled ESD pulses to equipment under test (EUT) via direct contact or air discharge. Key parameters include:
- Discharge Voltage Levels: Ranging from 2 kV to 30 kV, simulating real-world static buildup.
- Waveform Characteristics: Rise time (0.7–1 ns) and current decay (30–60 ns) must comply with standardized waveforms.
- Test Modes: Contact discharge (direct application) and air discharge (simulating sparks).
The LISUN ESD61000-2 complies with these standards, ensuring accurate replication of ESD events for validation testing.
Key Features of the LISUN ESD61000-2 Generator
The ESD61000-2 is engineered for precision and repeatability, with the following specifications:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Discharge Voltage Range | 0.1–30 kV (±5%) |
| Discharge Modes | Contact / Air Discharge |
| Output Polarity | Positive / Negative |
| Network Compliance | 330 Ω / 150 pF (IEC 61000-4-2) |
| Discharge Interval | 0.05–9.99 s (adjustable) |
| Display Resolution | 0.1 kV |
Competitive Advantages
- High Accuracy: ±5% voltage tolerance ensures reliable test conditions.
- Automated Testing: Programmable discharge sequences enhance efficiency.
- Robust Construction: EMI-shielded housing minimizes interference.
Industry-Specific Applications of ESD Testing
Medical Devices and Instrumentation
Medical electronics, such as patient monitors and diagnostic equipment, must withstand ESD events to prevent malfunctions. The ESD61000-2 verifies compliance with IEC 60601-1-2, ensuring operational safety in clinical environments.
Automotive and Rail Transit Systems
Modern vehicles incorporate sensitive control modules vulnerable to static discharge. Testing with the ESD61000-2 validates immunity in compliance with ISO 10605, reducing failure risks in critical systems.
Industrial Equipment and Power Tools
Heavy machinery and motor-driven tools are exposed to electrostatic buildup. The ESD61000-2 evaluates insulation integrity, preventing arc-induced damage in high-voltage environments.
Consumer Electronics and IT Equipment
Smartphones, laptops, and IoT devices undergo ESD testing to meet EN 55024 standards. The ESD61000-2 ensures robustness against user-induced static shocks.
Compliance with International Standards
The ESD61000-2 aligns with the following regulatory frameworks:
- IEC 61000-4-2 (General ESD immunity testing)
- ANSI/ESD S20.20 (ESD control programs)
- ISO 10605 (Automotive ESD testing)
- EN 61340 (Electrostatics in industrial applications)
Case Study: ESD Testing in Lighting Fixtures
LED drivers and smart lighting systems are susceptible to ESD-induced failures. A manufacturer used the ESD61000-2 to test a new high-bay luminaire, applying 8 kV contact discharges to control circuits. Post-test analysis confirmed compliance with IEC 60598-1, with no observed performance degradation.
Advanced Testing Methodologies
Human Metal Model (HMM) Simulation
The ESD61000-2 supports HMM testing, replicating discharges from charged personnel to metal components—a critical validation step for aerospace and defense applications.
System-Level ESD Testing
Integrated systems, such as communication base stations, require whole-device testing. The ESD61000-2’s programmable sequences facilitate multi-point discharge evaluations.
Comparative Analysis: ESD61000-2 vs. Competing Models
| Feature | ESD61000-2 | Competitor A | Competitor B |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage Range | 0.1–30 kV | 0.2–20 kV | 0.5–25 kV |
| Discharge Modes | Contact/Air | Contact Only | Contact/Air |
| Compliance | IEC 61000-4-2 | Partial | IEC 61000-4-2 |
| Programmability | Yes | No | Limited |
The ESD61000-2 outperforms alternatives in versatility and precision, making it ideal for multi-industry applications.
FAQ Section
Q1: What is the difference between contact and air discharge modes?
Contact discharge applies ESD directly via a probe, while air discharge simulates a spark gap. The ESD61000-2 supports both for comprehensive testing.
Q2: How does the ESD61000-2 ensure waveform accuracy?
Its built-in 330 Ω / 150 pF network conforms to IEC 61000-4-2, guaranteeing standardized current waveforms.
Q3: Can the ESD61000-2 test insulated devices?
Yes, air discharge mode evaluates non-conductive surfaces by generating sparks at specified distances.
Q4: What industries benefit most from automated ESD testing?
High-volume sectors like automotive and consumer electronics leverage programmable sequences for batch validation.
Q5: Is calibration required for the ESD61000-2?
Annual calibration is recommended to maintain ±5% voltage accuracy per ISO 17025 guidelines.