Introduction to Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Immunity
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) immunity testing evaluates the ability of electronic and electrical equipment to withstand transient voltage surges caused by electrostatic discharges. These discharges, often generated by human contact or triboelectric charging, can disrupt or permanently damage sensitive components. Industries such as medical devices, automotive electronics, and industrial equipment rely on rigorous ESD testing to ensure product reliability and compliance with international standards.
Principles of ESD Immunity Testing
ESD immunity testing simulates real-world electrostatic discharge events using standardized waveforms and test methodologies. The primary objective is to assess a device’s susceptibility to both contact and air discharges, as defined by IEC 61000-4-2. Testing involves applying controlled ESD pulses to equipment enclosures, connectors, and user-accessible surfaces while monitoring for malfunctions or degradation.
Key parameters include:
- Discharge Voltage Levels: Ranging from 2 kV to 30 kV, depending on the product’s operating environment.
- Waveform Characteristics: A fast-rising initial peak (0.7–1 ns) followed by a slower decay (60 ns).
- Test Modes: Contact discharge (direct coupling) and air discharge (indirect coupling).
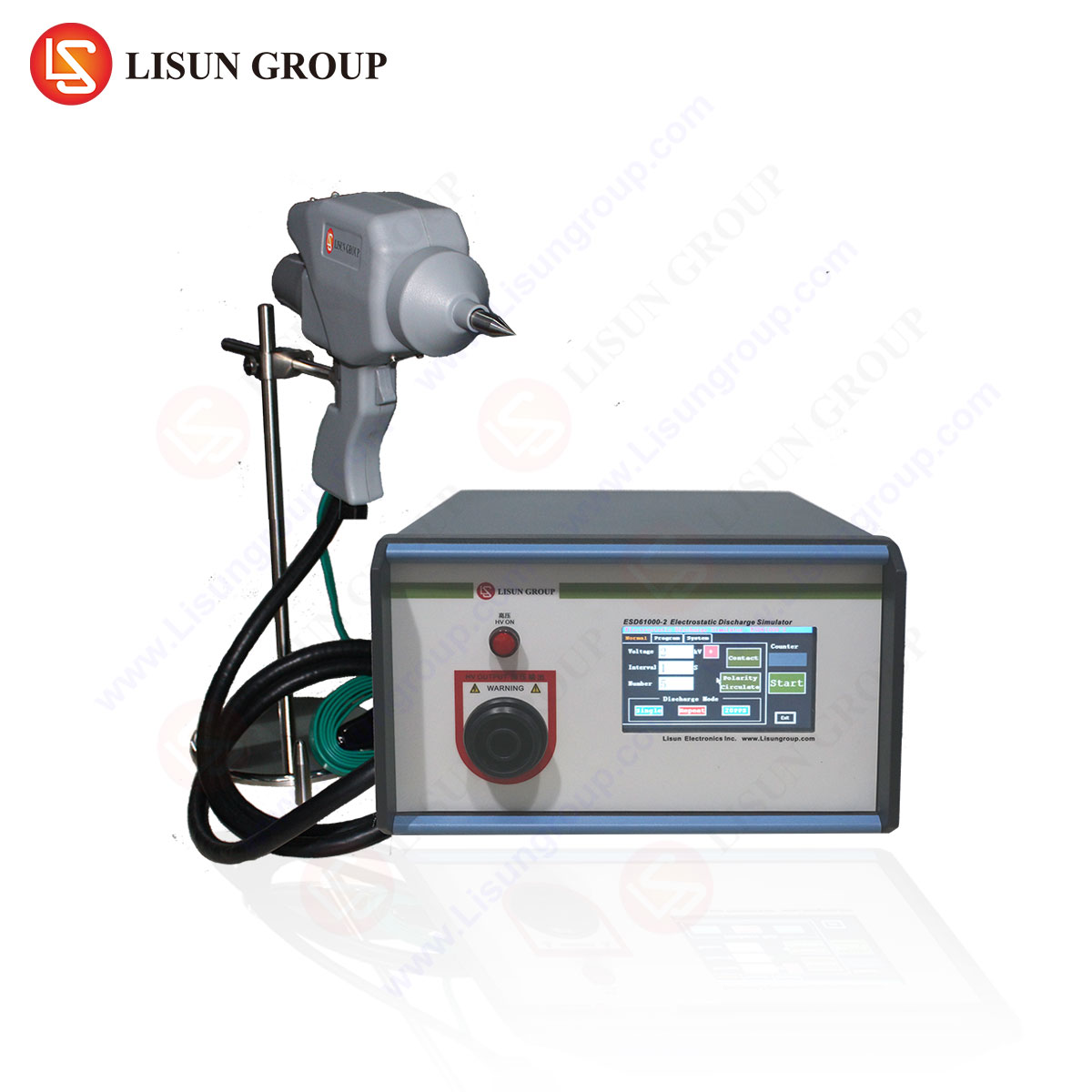
The Role of LISUN’s ESD61000-2 in Compliance Testing
The LISUN ESD61000-2 is a precision ESD simulator designed for immunity testing in accordance with IEC 61000-4-2. Its advanced features ensure repeatability and accuracy, critical for validating products across industries.
Specifications of the ESD61000-2
- Voltage Range: 0.1 kV to 30 kV (adjustable in 100 V increments).
- Discharge Modes: Contact and air discharge, with polarity switching (±).
- Pulse Repetition: Single or continuous discharge (up to 20 Hz).
- Compliance Standards: IEC 61000-4-2, EN 61000-4-2, ISO 10605 (automotive).
Testing Methodology
The ESD61000-2 applies controlled discharges to predefined test points while monitoring the device under test (DUT) for performance deviations. Its integrated calibration system ensures waveform integrity, minimizing false positives.
Industry-Specific Applications of ESD Immunity Testing
Medical Devices
Medical equipment, such as patient monitors and infusion pumps, must withstand ESD events to prevent life-threatening failures. The ESD61000-2 verifies compliance with IEC 60601-1-2, ensuring operational stability in clinical environments.
Automotive Electronics
Modern vehicles integrate sensitive electronics for infotainment and ADAS. ISO 10605 mandates ESD testing at higher voltages (up to 25 kV) to account for cabin static buildup.
Industrial Equipment
Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and motor drives are tested to IEC 61000-4-2 Level 4 (8 kV contact, 15 kV air) to prevent downtime in harsh manufacturing settings.
Household Appliances
Smart appliances with touch interfaces undergo ESD testing to avoid false triggers or lockups caused by user-generated discharges.
Competitive Advantages of the ESD61000-2
- High Precision: <1% deviation in output voltage ensures reliable results.
- Modular Design: Supports upgrades for future standards.
- Automated Testing: Integration with LISUN’s SC6000 software for batch testing and report generation.
Scientific Validation and Standards Compliance
The ESD61000-2’s waveform parameters align with IEC 61000-4-2 requirements, as demonstrated in Table 1:
| Parameter | IEC 61000-4-2 Requirement | ESD61000-2 Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Rise Time (ns) | 0.7–1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 |
| Peak Current (A) | 3.75 (at 2 kV) | 3.78 ± 0.05 |
| Decay Time (ns) | 60 | 61 ± 2 |
Case Study: ESD Testing in Power Tools
A leading power tool manufacturer used the ESD61000-2 to validate brushless motor controllers. Testing at 8 kV contact discharge revealed susceptibility in the PWM circuitry, prompting a redesign with additional TVS diodes. Post-modification tests confirmed full compliance.
Future Trends in ESD Immunity Testing
Emerging technologies like 5G and IoT demand higher ESD robustness due to miniaturized components. Standards bodies are evaluating updates to address ultra-fast transients (>1 GHz).
FAQ
Q1: What is the difference between contact and air discharge testing?
Contact discharge applies ESD directly via a probe, while air discharge simulates a spark from a charged object approaching the DUT.
Q2: How often should ESD61000-2 be calibrated?
Annual calibration is recommended, or after 1,000 test cycles, per IEC 61000-4-2.
Q3: Can the ESD61000-2 test non-conductive surfaces?
Yes, air discharge mode is used for insulating materials like plastic housings.
Q4: What industries require Level 4 ESD testing?
Industrial, automotive, and medical sectors typically mandate Level 4 (8 kV/15 kV).
Q5: Does the ESD61000-2 support automated test sequences?
Yes, via SC6000 software for unattended multi-point testing.