Fundamentals of Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Testing
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a transient electrical phenomenon that occurs when two objects with differing electrostatic potentials come into contact or proximity, resulting in a rapid transfer of charge. ESD events can cause catastrophic failures or latent defects in electronic components, necessitating rigorous testing to ensure product reliability.
The ESD gun, a critical tool in compliance testing, simulates human-body-model (HBM) and machine-model (MM) discharge events per IEC 61000-4-2 and ANSI/ESD STM5.1 standards. These tests evaluate a device’s immunity to electrostatic discharges encountered during manufacturing, handling, or operation.
Operational Principles of ESD Guns
An ESD gun generates controlled high-voltage discharges through a relay-switched network, replicating real-world ESD events. The discharge waveform consists of a fast rise time (<1 ns) and a subsequent current decay, simulating the energy transfer from a human operator or conductive tool.
Key parameters include:
- Discharge Voltage: Adjustable from 2 kV to 30 kV, covering standard test levels.
- Discharge Modes: Contact discharge (direct coupling) and air discharge (spark-gap coupling).
- Current Waveform Compliance: Adherence to IEC 61000-4-2’s specified 4 kV/8 kV current profiles (e.g., 3.75 A/ns rise time).
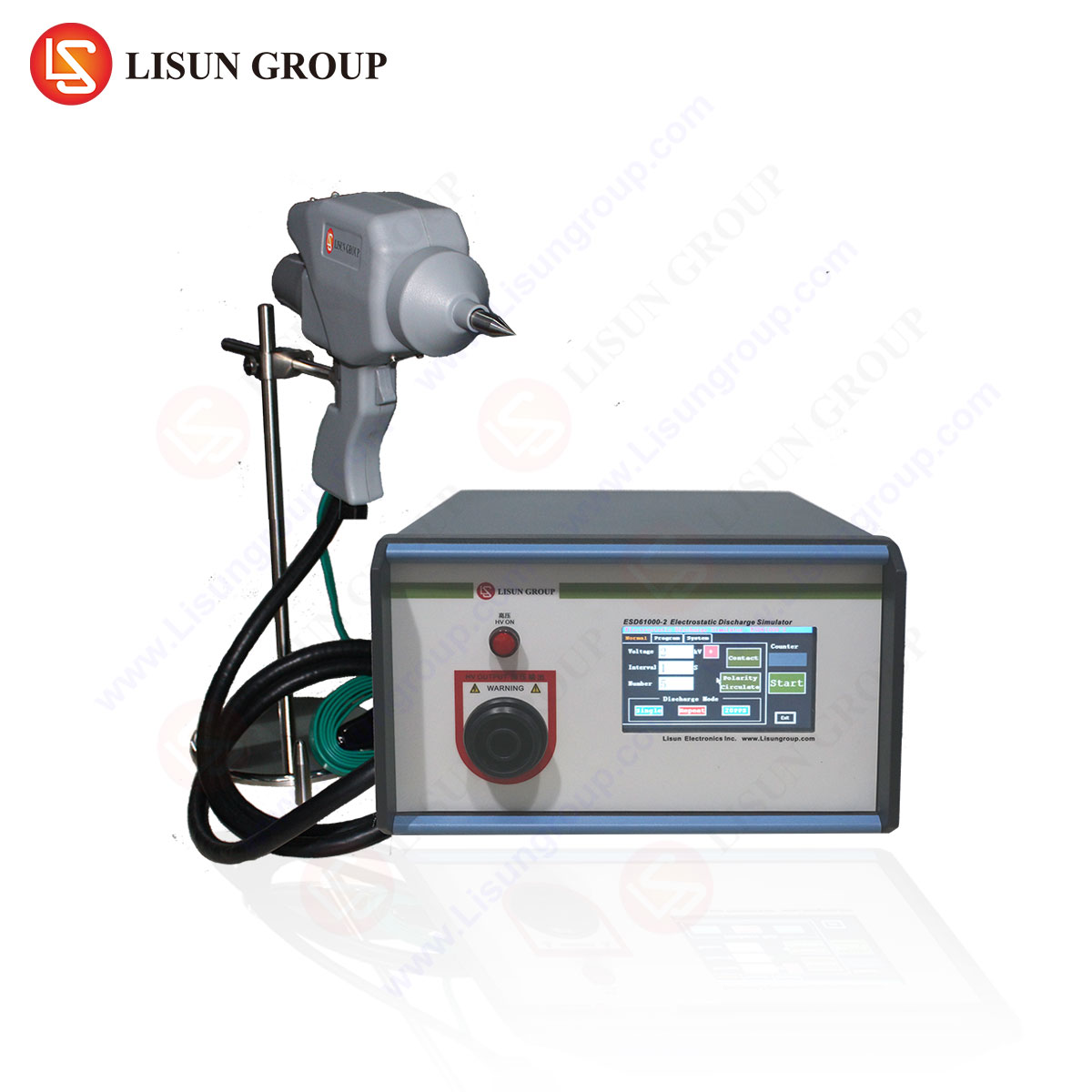
LISUN ESD61000-2: Technical Specifications and Testing Capabilities
The LISUN ESD61000-2 is a precision ESD simulator designed for compliance testing across multiple industries. Its specifications include:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Voltage Range | 0.1–30 kV (±5%) |
| Discharge Modes | Contact/Air |
| Polarity | Positive/Negative |
| Current Waveform | IEC 61000-4-2 Compliant |
| Test Repetition Rate | 20 discharges/sec (max) |
| Operating Environment | 15–35°C, 30–60% RH |
The ESD61000-2 integrates advanced discharge control, ensuring repeatable test conditions for automotive, aerospace, and medical device validation.
Industry-Specific Applications of ESD Testing
Automotive and Rail Transit Systems
Modern vehicles incorporate sensitive electronic control units (ECUs) vulnerable to ESD. The ESD61000-2 validates immunity in infotainment systems, powertrain modules, and ADAS sensors per ISO 10605.
Medical Devices and Instrumentation
Implantable devices and diagnostic equipment must withstand ESD during surgical handling. IEC 60601-1-2 mandates testing up to 8 kV (contact) and 15 kV (air).
Industrial and Power Equipment
Variable-frequency drives (VFDs) and PLCs are tested for ESD robustness to prevent malfunctions in harsh environments.
Consumer Electronics and IT Equipment
Smartphones, routers, and audio-visual devices undergo ESD testing to mitigate failures from user interactions.
Comparative Advantages of the LISUN ESD61000-2
- Enhanced Waveform Accuracy: Proprietary circuitry ensures ±5% deviation from IEC 61000-4-2’s current waveform requirements.
- Automated Test Sequencing: Programmable discharge patterns reduce operator variability.
- Multi-Standard Compliance: Supports ISO, ANSI/ESD, and MIL-STD-883H protocols.
- Robust Construction: EMI-shielded housing minimizes external interference.
Standards and Regulatory Compliance
The ESD61000-2 aligns with:
- IEC 61000-4-2 (Immunity Testing)
- ANSI/ESD STM5.1 (HBM Evaluation)
- ISO 10605 (Automotive ESD)
- IEC 60601-1-2 (Medical Devices)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the difference between contact and air discharge testing?
Contact discharge applies ESD directly via a conductive tip, while air discharge simulates sparks through an air gap.
Q2: How does the ESD61000-2 ensure waveform compliance?
Built-in calibration monitors current rise time (0.7–1 ns) and peak amplitude per IEC 61000-4-2.
Q3: Which industries require ESD testing above 15 kV?
Aerospace (MIL-STD-883H) and high-voltage power equipment often demand 20–30 kV testing.
Q4: Can the ESD61000-2 simulate charged-device model (CDM) events?
No, CDM testing requires specialized equipment like the LISUN ESD-CDM.
Q5: What maintenance is required for long-term accuracy?
Annual recalibration and relay inspection are recommended to prevent waveform degradation.