Introduction to ESD Gun Testing and Its Industrial Relevance
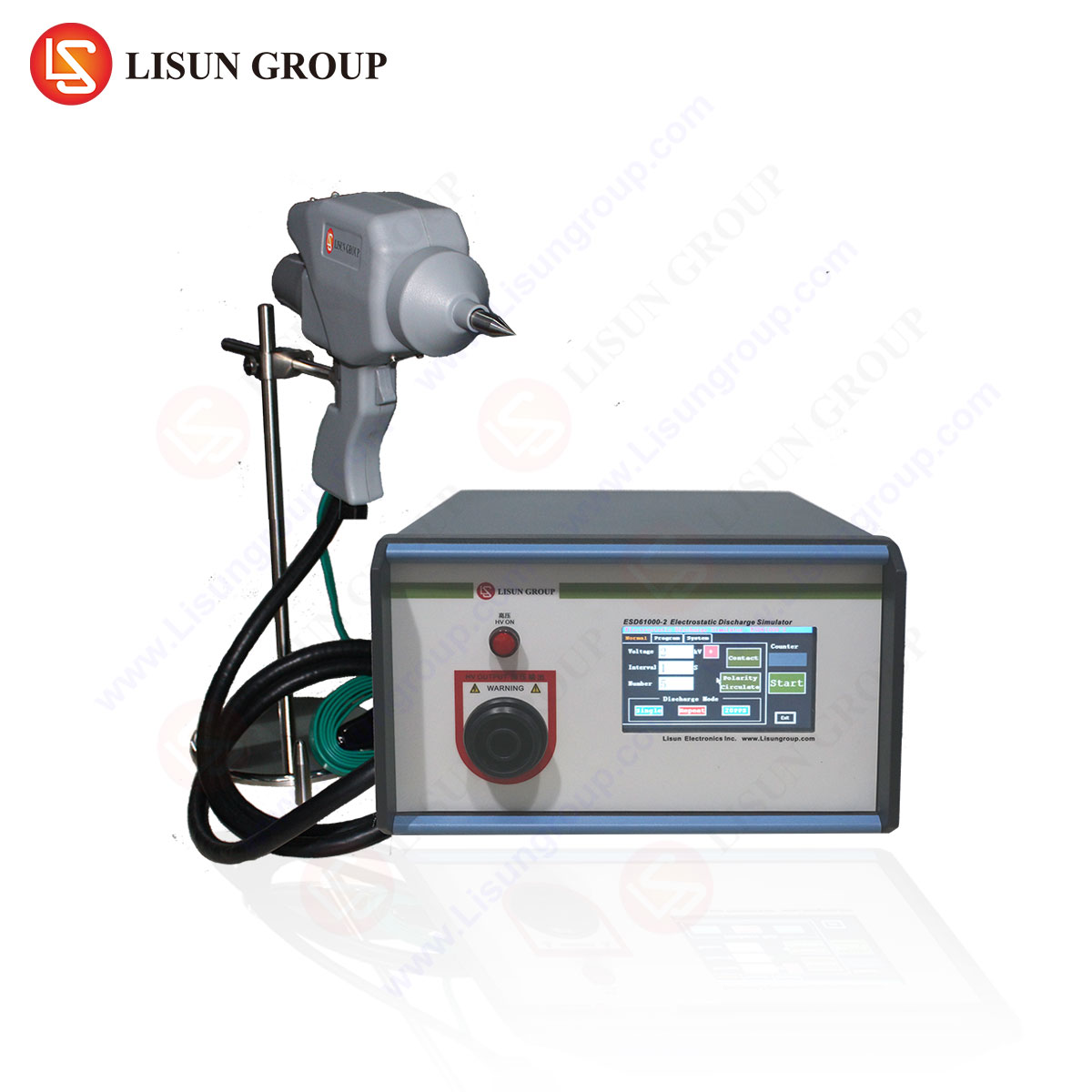
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) poses a significant risk to electronic and electrical equipment across multiple industries, including automotive, medical devices, industrial automation, and consumer electronics. ESD gun testing simulates human-body-model (HBM) discharges to evaluate a device’s immunity to transient electrical disturbances. This article presents a rigorous methodology for ESD testing, with a focus on the LISUN ESD61000-2 ESD simulator, a high-precision instrument designed for compliance with IEC 61000-4-2 and other international standards.
Fundamental Principles of ESD Gun Testing
ESD testing replicates electrostatic discharges that occur when a charged human body or object comes into contact with electronic equipment. The LISUN ESD61000-2 generates controlled discharge pulses with adjustable voltage levels (up to ±30 kV) and waveform characteristics to assess immunity. Key testing principles include:
- Contact Discharge: Direct application of ESD pulses via a pointed electrode.
- Air Discharge: Simulating indirect discharges through air gaps.
- Waveform Compliance: Ensuring discharge pulses meet IEC 61000-4-2 rise time (0.7–1 ns) and current (30 A at 8 kV) specifications.
LISUN ESD61000-2: Key Specifications and Competitive Advantages
The LISUN ESD61000-2 is engineered for high repeatability and accuracy, making it suitable for industries requiring stringent ESD immunity validation. Its specifications include:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Voltage Range | ±0.1 kV to ±30 kV |
| Discharge Modes | Contact, Air |
| Compliance Standards | IEC 61000-4-2, ISO 10605, EN 61000-4-2 |
| Waveform Accuracy | ±5% deviation from standard |
| Application Industries | Automotive, Medical, IT, Industrial Controls |
Competitive Advantages:
- High Repeatability: Minimizes test result variability.
- Multi-Standard Compliance: Supports automotive (ISO 10605) and industrial (IEC 61000-4-2) testing.
- User-Configurable Parameters: Adjustable discharge intervals and polarity settings.
Test Setup and Environmental Considerations
Proper test configuration is critical for reliable ESD immunity assessment. The following conditions must be met:
- Grounding: A low-impedance ground plane (copper or aluminum) must be used.
- Test Surface: Non-conductive, 0.5 m above the ground plane.
- Humidity Control: Maintained at 30–60% RH to prevent false discharges.
The LISUN ESD61000-2 integrates seamlessly into test benches, featuring ergonomic design for operator safety and precision.
ESD Test Procedure: Step-by-Step Methodology
1. Pre-Test Verification and Calibration
- Verify the ESD gun’s waveform using an oscilloscope and current target (per IEC 61000-4-2).
- Confirm voltage accuracy (±5% tolerance).
2. Selection of Test Points
- Direct Discharge Points: Exposed conductive surfaces (e.g., metal housings).
- Indirect Discharge Points: Nearby coupling planes (horizontal/vertical).
3. Discharge Application Protocol
- Apply 10 single discharges per test point (positive and negative polarity).
- For air discharge, approach the EUT at 5 mm/s until discharge occurs.
4. Performance Evaluation Criteria
- Class A: No degradation (full functionality).
- Class B: Temporary disruption (self-recovery).
- Class C: Reset or manual intervention required.
Industry-Specific Applications of ESD Testing
Automotive Electronics (ISO 10605 Compliance)
- Evaluates infotainment systems, ECUs, and sensors against 15 kV air discharges.
Medical Devices (IEC 60601-1-2)
- Validates patient monitoring equipment against 8 kV contact discharges.
Industrial Automation (IEC 61000-4-2)
- Tests PLCs and motor drives for immunity to 30 kV transient events.
Common ESD Test Failures and Mitigation Strategies
- Soft Errors (Data Corruption): Implement shielding or ferrite beads.
- Hardware Damage (Component Failure): Redesign PCB layouts with ESD protection diodes.
FAQ Section
Q1: What is the difference between contact and air discharge testing?
- Contact discharge applies ESD directly to conductive surfaces, while air discharge simulates indirect discharges through non-conductive gaps.
Q2: How often should the LISUN ESD61000-2 be calibrated?
- Annual calibration is recommended, with waveform verification before critical tests.
Q3: Can the ESD61000-2 be used for automotive ESD testing?
- Yes, it complies with ISO 10605 for automotive component validation.
Q4: What industries require the highest ESD test voltages?
- Industrial equipment (30 kV) and aerospace (25 kV) demand the most stringent testing.
Q5: How does humidity affect ESD test results?
- Low humidity increases static buildup, while high humidity may suppress discharges, requiring controlled test conditions.
This methodology ensures robust ESD immunity validation, leveraging the LISUN ESD61000-2 for precision and compliance across critical industries.